Press Release
Hyundai E&C to Tackle Global Greenhouse Gas Reduction Efforts with World`s First Floating CCS Technology
▲ Leads national research initiative into floating-body based CCS design technology, from ship-based models to the world's first floating concrete structures
▲ Secures Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) capabilities and accelerates next-generation energy projects in line with the global push for carbon neutrality
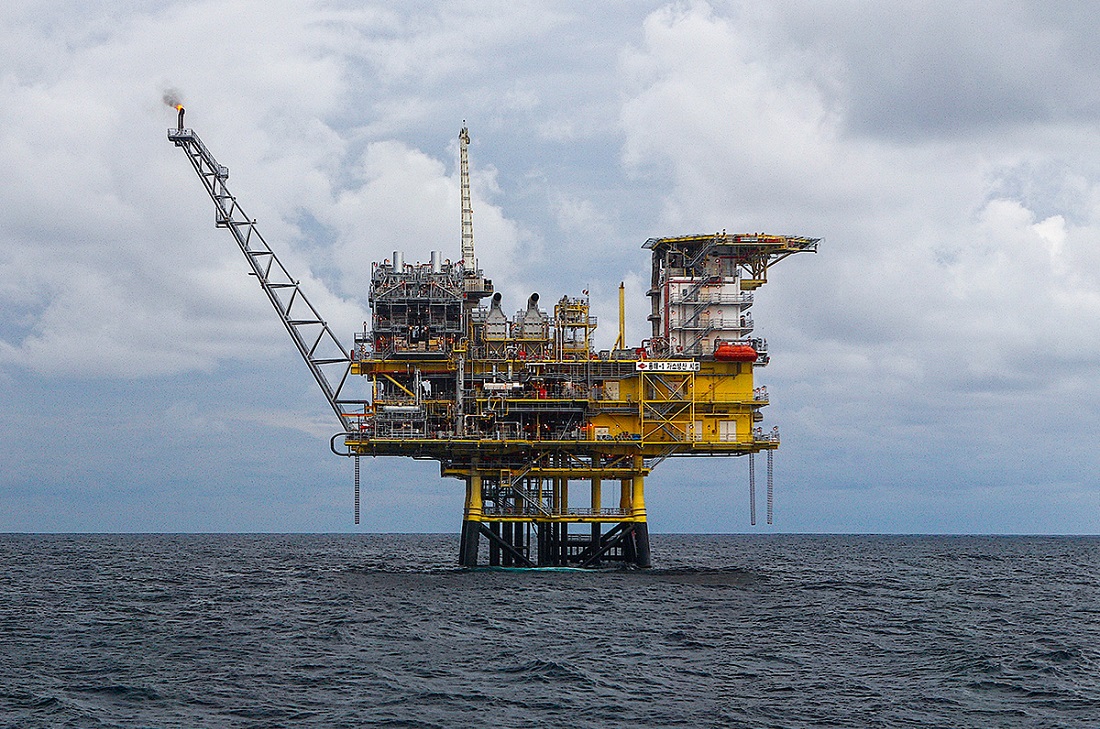

Hyundai E&C is set to contribute to greenhouse gas reduction efforts by leveraging floating-body based CCS1) technology to utilize depleted oil and gas fields in Southeast Asia's maritime regions.
Hyundai E&C announced on the 13th that it has signed an agreement with the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning, under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE), for the ‘Development of Conceptual/Basic Design Technology for Sequentially Transferable, Expandable Floating CCS Facilities and CO₂ Injection for the Operation of Distributed CCS Repositories in Southeast Asia.’ The company stated that it will conduct a 42-month international joint research project with eight institutions from the private, public, and academic sectors. CCS technology involves capturing emitted carbon dioxide and safely injecting it deep underground for permanent storage.
This national research initiative, undertaken by Hyundai E&C, aims to secure the conceptual and Front-End Engineering & Design (FEED) technology for a floating CO₂ injection system designed to utilize depleted oil and gas fields in Southeast Asia's maritime regions as carbon dioxide repositories. The total research budget for this initiative amounts to KRW 5.8 billion. As the lead research institution, Hyundai E&C will oversee the entire project, with eight institutions, including Korea National Oil Corporation, the American Bureau of Shipping, Seoul National University, and Indonesia's Pertamina University (established by Indonesia’s national oil company Pertamina), participating as joint researchers.
Until now, offshore carbon dioxide storage has involved injecting CO₂ through fixed subsea structures and pipelines. However, in regions like Southeast Asia where storage sites are geographically dispersed, a floating system that allows modular injection facilities to be sequentially moved and utilized is significantly more efficient.
In this initiative, in addition to utilizing ship-based floating bodies, Hyundai E&C plans to develop the world's first CO₂ injection system using floating concrete structures that can be deployed at sea and aims to derive a viable business model by securing Approval In Principle (AIP) before commercialization. More specifically, since this approach is projected to reduce infrastructure construction costs by up to 25% compared to existing fixed methods, it is expected to serve as a catalyst for expanding CCS projects in Indonesia and across Southeast Asia.
In addition, this floating CCS technology has improved levels of applicability to blue hydrogen and blue ammonia projects. This is because establishing infrastructure capable of directly handling carbon dioxide generated during the hydrogen or ammonia production process at sea would minimize carbon emissions throughout the entire cycle of production, storage, and transport. Through this research, Hyundai E&C is considering expanding its vision to include offshore carbon-neutral clusters, such as floating hydrogen production and offshore ammonia synthesis facilities.
A Hyundai E&C official stated, “Floating CCS technology is a meaningful leap forward made possible by Hyundai E&C precisely because of our competitive strengths in offshore civil engineering and a wide range of plant sectors.” The official added, “By successfully completing this project, we will not only contribute to securing carbon credits by applying it to ‘cross-border CCS’ projects that transport and store domestic CO₂ overseas but also position our technology as a bridgehead for entering the global carbon reduction market.”
Since 2022, Hyundai E&C has been conducting CCUS2) research in cooperation with Malaysia, the Netherlands, and others to utilize depleted oil and gas fields. Since 2023, the company has expanded its standing as a leader in the field by participating in the ‘Basic Design of the East Sea Gas Field CCS Demonstration Project,’ Korea's first commercial CCS project. Moreover, it is also undertaking the national research initiative for the ‘Development of CO₂ Capture, Liquefaction, and Utilization Technology for Blue Hydrogen Production,’ diligently working to secure capabilities across the entire CCUS value chain.
Hyundai E&C plans to align with the government's carbon-neutral policy by further developing its core CCUS technologies and expanding its business scope through an energy mix that includes nuclear power, hydrogen, and renewable energy, while strengthening its global competitiveness in projects aimed at addressing the climate crisis.
1) CCS: Carbon Capture and Storage
2) CCUS: Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage